Proteoglycan (PG) is a hybrid molecule composed of a central core protein by bonding it with glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) with a covalent bond.1Cartilage is composed of more than 90% dry weight of proteoglycans,2 which is the core structure in the extracellular matrix. PG in vertebrates can be characterized by the type of glycosami- noglycans that bind to the core protein structure in 5 groups: hyaluronan (HA), chondroitin sulfate (CS), keratan sulfate (KS), dermatan sulfate (DS), and heparan sulfate (HS).3 The PG that has been found in fish cartilage are chondroitan sulfate (CS) and dermatan sulfate (DS).4
In 1992, Japanese researchers discovered and developed PG extraction from the nasal tip cartilage of Oncorhynus keta (salmon) for commercial uses and named it “Proteoglycan-IPC” (IchimaruPharcos Co, LTD., Gifu, Japan). This material has been added to cosmetics to provide wrinkle relief and promote collagen synthesis.5
In 2018, Chuenwattana et al.,1 discovered and developed PG extraction from the head of Trichopoduspectoralis (Snakeskin gourami). This material has been added to anti-aging facial mask for wrinkle relief and to promote collagen synthesis. The results from this study demonstrated that PG extract from Trichopoduspectoralis has low potential skin sensitization and accelerated collagen synthesis in rat models. These results, however, do not have scientific findings regarding potential skin sensitization in human.
The aim of this study is to evaluate potential skin sensitization of applied PG facial mask extracted from Trichopoduspectoralis using modified HRIPT.
Ingredients of PG facial mask patch test
The ingredients of PG facial mask patch test comprise PG solution, Glyceryl monostearate, Propylene glycol, PVM/MA Copolymer, Glycerine, Butylene glycol, Carbomer, Polysorbate 20, Disodium EDTA (2NA EDTA), DMDM Hydantoin, and Iodopropynyl butylcarbamate.
Study population
All140 of the healthy male and female volunteers between the ages of 18 to 60 were enrolled. The subjects were informed of the HRIPT, including possible adverse skin reactions from this experiment. Written informed consent was obtained. Additionally, other criteria included the stipulation that the volunteers needed to dependable, able to read, understand, and follow instructions in Thai. Prior to starting the test, each volunteer had to complete a medical history form. The subjects needed to meet all of the inclusion and exclusion criteria listed below.
Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
HRIPT studies
Induction phase
The HRIPT was used to assess the skin sensitization potential of the PG facial mask, which was modified from Politano and Api.6 The test article contained material per patch of 0.3 ml, size 1x1 cm2. Healthy volunteers, male and female applied the patch tests. The placebo patch tests (containing 0.9% normal saline) were applied on normal skin at left scapula and applied PG facial mask patch tests were applied to normal skin at right scapula. Healthy volunteers applied patch tests on Monday, Wednesday, and Friday for three consecutive weeks. All of the patch tests were removed 24 h after having been applied and HRIPT scoring was evaluated (Table 1). This procedure was repeated until 9 induction applications of the test article were made.
Challenge phase
10 to 14 days after induction phase, a single challenge patch was applied to a naïve site of normal skin on left scapula (placebo patch tests) and applied PG facial mask patch on right scapula. The healthy volunteers were instructed to return to the testing facility 24 h later for removal of the patch tests by the evaluator. The challenge site is scored 24, 48, and 72 h after the material was applied and the experiment monitor was present at the 72 h reading HRIPT score.
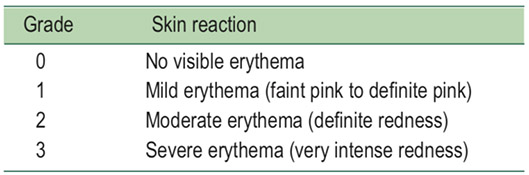
Erythema scale: this scale is used only for grading degree of erythema (redness). A score on this scale will be assigned following every application of a test material.6,7
Table 1: HRIPT scoring scale:
Statistical analysis
Results are expressed as means ± SD. Data were analyzed using independent t test, and using SPSS for Windows, ver. 11. Values of p < 0.05 were considered to be significant.
All 140 healthy volunteers completed the study. The age of subjects ranged from 19 to 26 years old (mean age 21.59 ± 1.9 years old) with the majority of 128 females (91.4%) and 12 males (8.6%). The demographic data of healthy volunteers are listed in Table 2. The healthy volunteers had atopic history 26 (18.6%), atopic dermatitis 27 (19.3%), allergic rhinitis 28 (20%), allergic conjunctivitis 6 (4.3%), family history of allergy 18 (12.9%), previous skin care products allergy 48 (34.3%), and previous sunscreen allergy 21 (15.5%), respectively (Table 2).
Table 2: Demographic data of healthy volunteers (n = 140).

Table 3: HRIPT scoring scale
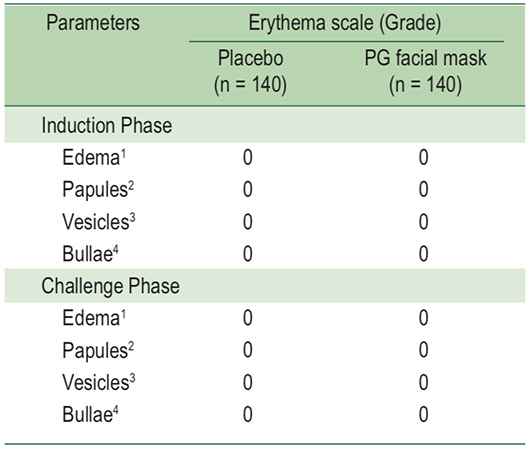
1 Edema: definite swelling
2 Papules: many small, red, solid elevations; surface of reaction has granular feeling
3 Vesicles: small circumscribed elevations having translucent surfacesso that fluid is visible (blister-like); vesicles are no larger than 0.5 cm in diameter
4 Bullae: vesicles with a diameter > 0.5 cm; vesicles may coalesce to form one or a few large blisters that fill the patch site
The HRIPT scoring scale of induction phase and challenge phase, edema, papules, vesicles, and bullae of healthy volunteers who applied PG facial mask were not significantly different when compared to the placebo patch test group (Table 3).
The results of the HRIPT study are presented as the number of induced skin sensitization reactions observed out of the total number of volunteers who have completed the study. The induction phase of skin sensitization is determined by enhancement of the skin reaction, edema, papules, vesicles, or bullae reaction, observed at challenge phase greater than that observed during Induction phase. If the reaction occurs during the early part of the induction phase this is confirmed at the challenge phase.6
In 1945, Henders and Riley8 used the patch test to evaluate skin irritation and sensitization properties of materials and chemical agents. If a positive result were recorded among the healthy volunteers, it would have indicated that materials or chemical agents were skin sensitizing or irritating. However, if a negative result were recorded among healthy volunteers, for example in a sample of 100 healthy volunteers, it would have indicated that these materials and chemical agents were low skin sensitizing or irritating.
In this study, 100% of healthy volunteers completed the study phases. In the induction phase, the HRIPT scoring scale was 0 on all of observational studies if the PG facial mask had a negative skin sensitization on healthy volunteers. This study has confirmed the negative result and the lack of a sensitization reaction in humans. HRIPT scoring scale of the challenge phase confirmed the results of skin sensitization in the induction phase: 100% of healthy volunteers recorded negative skin sensitization. Therefore, the PG facial mask has a low skin sensitization according to the HRIPT test.
The results from this study demonstrate that PG facial mask containing PG solution extracted from Trichopoduspectoralis has low potential skin sensitization. Further investigation of the potential skin sensitization of PG facial mask among large population is required.
This study was supported by a grant from Bansomde- jchaopraya Rajabhat University, Bangkok, Thailand Fund. We are very thankful to Assistant Professor Dr.Narongpon Dumavibhat, Dr.Sirawit Stitsmith and Mrs.Angkana Jongsawadipatana for statistical analysis.